Textile pest experts Melbourne
What Are Textile Pests?
Textile pests are insects like moths and beetles whose larvae possess digestive systems containing a mixture of bacteria and chemicals, designed to break down natural fibres into components that offer the larvae a source of essential nutrients.
The digestive processes involved are highly complex and each insect has a slightly different way of doing the job properly.
What Materials Do Textile Pests Eat?
The primary material being digested is keratin, a protein component of feathers, hair, fur, horns, antlers, hooves, nails and even beaks, although the plant derived products, such as the expensive flooring product sisal is also at risk.
Where Do Textile Pests Come From?
Textile pests are found widely in the environment, so are not simply imported with foreign textiles or brought into your home with new carpets.
When Are Textile Pests Most Active?
We see these pests more active when the temperatures rise , although these insects will remain active throughout the year indoors.
Infestations can be difficult to spot in many homes until the damage is all too apparent and you lift up a sofa or bed to find the textile looking a little fluffy - but it is only when you vacuum you finally discover a very large bald patch, often requiring that the whole carpet be replaced.
Moths are normally seen at night flying around computer monitors or TV screens and the beetles are often found on window sills. Most properties will have these insects, yet numbers will be very small and damage not noticeable. In large infestations however, dozens or even hundreds of moths, beetles and larvae will be discovered.
Where Are Textiles Most At Risk?
Stored textiles in lofts and cellars, are very often most at risk. Undisturbed, and dark, they create ideal conditions for infestations to develop that will ultimately infest the textiles of the main living areas
What Should I Do If I Find Them?
Early intervention is essential to the success of any control, so contact us to carry out a thorough inspection of the property and if required we can advise you about the key options available to your particular situation.
How Do I Get Rid of Textile Pests?
Residual insecticides and rapid knock down fumigation are among the methods open to us in the crusade against textile pests. In general you need to use a variety of treatment methods to achieve a high degree of control and of course the more thorough the treatment the more it will cost.
Damaged textiles cost thousands to replace so any treatment that prevents a total loss will remain good value for money. Even if you decide to throw out the carpet or other textiles it is well worth having the area treated to control any traces of infestation left that only experts like us at Redknight can spot
Evidence of textile Pest Activity
: • the presence of the actual insect, alive or dead, at various stages of its development
• cast skins or other body parts
• chewing marks
• exit holes in surfaces of wood
• Hair, fur or feather loss
• webbing
• grazed” surfaces
• Frass (debris or excrement produced by insects, usually a soft powdery material)
• faecal pellets, dried stains or faecal spots It is usually these signs, rather than the actual pest, that are detected first. Be familiar with the signs and inspect for pest evidence to detect activity and locate the source of the infestation.
Most common Textile Pest Species

Case-bearing clothes moth
(Tinea pellionella)
Characteristics
- They are greyish-brown to dark in colour, about 7-10mm in body length
- Dislikes light and frequent dark areas. Often scurries across surfaces instead of flying when disturbed
- Larvae between 7-10mm, cream caterpillar with dark brown head , lives in small case or cocoon its entire life, and carries this around with it, prefers undisturbed areas.
- Adult lifespan 3-8 months


Common clothes moth
(Tineola bissellietta)
Characteristics
- They are golden-buff in colour, about 8-10mm in body length
- Similar behaviour to case-bearing clothes moth
- Larvae between 7-10mm, cream translucent caterpillar with dark brown head, lives in a network of tunnels or tubes it constructs, and is difficult to see.
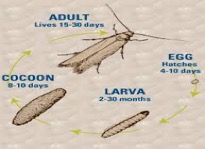

Variegated carpet beetle
(Anthrenus verbasci)
Characteristics
- Very small beetle, brown, grey and black mottled back.
- Very slow moving, often seen at windows trying to get outside to pollen on flowers.
- Larvae between 3- 4.5 mm, resembles a beetle more than a caterpillar.
- Adult lifespan, 9-12 months.

Chemical Control
Our chemical control solutions involve the careful use of insecticides in areas identified with signs of an infestation. Insecticides may be applied through the method of surface or space sprays or dusts.
Furniture may have to be moved and carpets and rugs pulled back to ensure appropriate treatment to all affected areas.
We advise our customers to de-clutter and ensure a thorough vacuuming of all carpet areas prior to insecticidal treatment.
- Surface sprays - surface sprays for insecticidal treatment are usually used when clothes moths or carpet beetles have been identified as the invading pest species. This treatment is commonly applied to areas in your property where textile pests are known to feed.
- Space sprays - we use space sprays to kill moths or beetles that have been spotted on ceilings, walls or furnishings. It is used together with other applications to ensure penetration of infested fabric items are dealt with effectively.
- Dusts - insecticidal dusts containing an insect growth regulator is very effective in a roof cavity when theres an infestation due to the presence of bird nesting .
Species of Textile Pests
There are at least ten types of textile pests that have been recorded in Australia. It is mainly the introduced species, which are commonly found in homes or businesses.
The Most Frequently encountered species include:
- Case-bearing clothes moth
- Variegated carpet beetle
- Common or webbing clothes moth
Less encountered species include:
- Brown house moth (Hofmannophila pseudospretella)
- Australian carpet beetle (Anthrenocerus australis)
- Furniture carpet beetle (Anthrenus flavipes)
- Black carpet beetle (Attagenus piceus)
- Tapestry moth (Trichopaga tapetzella)
Experts in Textile Pest control in Melbourne,Ballarat and Geelong - Redknight
All treatment comes with warranties.
